eCommerce in Africa
Jumia Business Analysis: Top Markets, Revenue, GMV & eCommerce in Africa
Jumia's GMV growth faltered post-pandemic, but a shift to a third-party marketplace and rising JumiaPay usage offer hope for recovery in Africa's eCommerce space.
Article by Cihan Uzunoglu | October 17, 2024Download
Coming soon
Share
Jumia Business Analysis: Key Insights
GMV Development and Marketplace Strategy: Jumia experienced significant GMV growth before the pandemic, but post-pandemic declines have slowed momentum. The company is shifting towards a third-party marketplace model to drive gradual recovery.
Market Presence and Top Products: Nigeria remains Jumia’s largest market, followed by Morocco, Kenya, Egypt, and Ivory Coast. Electronics lead Jumia’s top-selling categories in 2023, with personal care, leisure items, fashion, and household goods also performing well.
Recent Developments and Zando's Role: In Q1 2024, Jumia saw a 5% GMV increase and 52% growth in JumiaPay transactions. Jumia discontinued Jumia Food to focus on more profitable areas, while Zando, a Jumia Group member, led online fashion retail in South Africa before the shutdown decision.
Jumia, a leading pan-African eCommerce company, has been making headlines since becoming Africa's first unicorn, surpassing a valuation of US$1 billion. It is also the first African start-up to be listed on the New York Stock Exchange. While it may not rank among the largest global online marketplaces by GMV, Jumia is one of the most valuable German eCommerce companies.
With over 64,000 sellers and millions of customers, Jumia ensures efficient deliveries across Africa. How did the company transform from a first-party retailer into a dynamic third-party marketplace? What strategies and challenges have shaped its growth?
What is Jumia Marketplace?
Jumia is a pan-African eCommerce platform operating in 11 African countries. Based in Berlin, the company leverages technology to provide innovative, convenient, and affordable online services in Africa. Jumia also supports business growth by helping sellers reach and serve customers more effectively through its platform.
Jumia’s platform includes a marketplace that connects over 64,000 sellers with customers, a comprehensive logistics network for efficient shipment and delivery of packages, and JumiaPay, a proprietary payment service that facilitates transactions across select markets on the platform.
Jumia GMV: Pre-Pandemic Growth Didn’t Last
Despite growing at an impressive rate before the pandemic, Jumia couldn’t sustain its success:
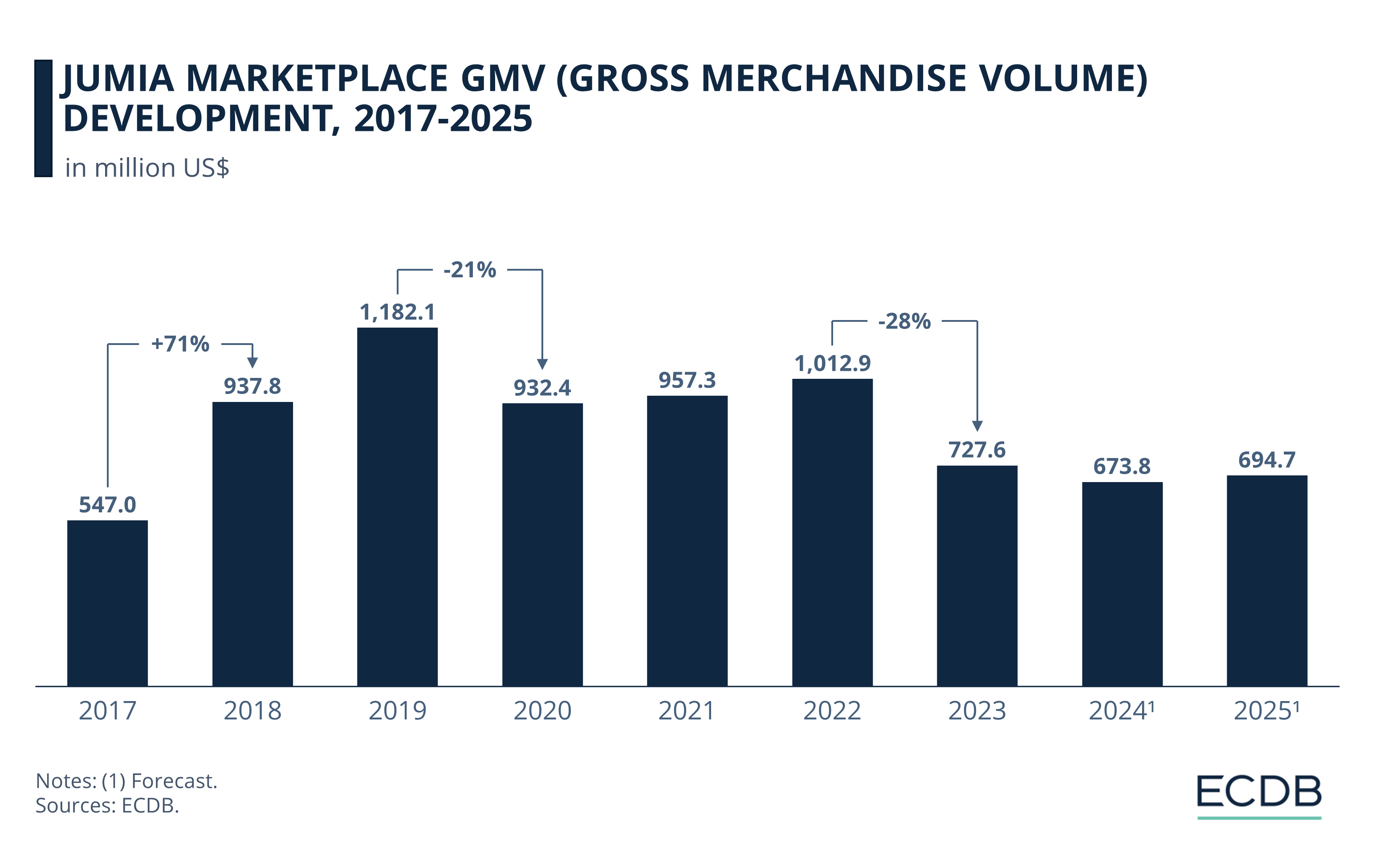
Jumia's GMV (Gross Merchandise Volume) of US$547 million in 2017 increased by 71% in the following year, reaching US$937 million by 2018.
Continuing its success with a more modest growth rate (26%) in 2019, Jumia suffered a 21% decline in GMV, dropping to US$932 million by 2020.
With minimal growth rates through 2021 and 2022, Jumia contracted by 28% last year.
While our forecast for 2024 shows a further 7.4% decline in GMV, Jumia should bounce back next year as we forecast 3.1% growth.
Increase in Third-Party Activity
Originally a first-party online retailer, Jumia shifted towards a more third-party marketplace strategy in 2016.
Jumia balances between first-party and marketplace channels. Country-by-country, market-by-market, Jumia looks for the channel split that creates the most value for customers and presents the best opportunity for the category mix. This dynamic strategy is reflected in the evolving distribution of Jumia’s marketplace GMV.
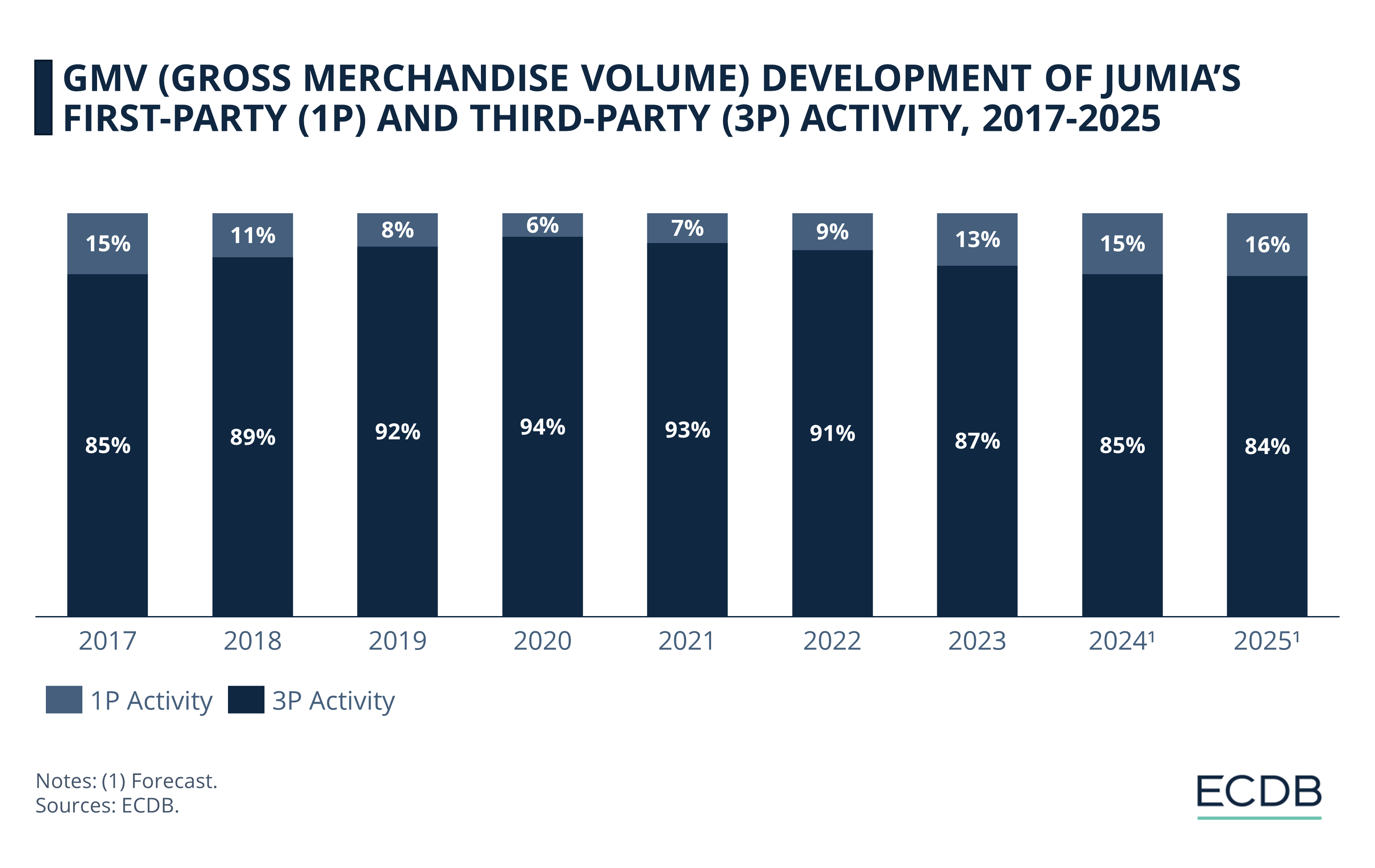
In 2017, first-party activity on Jumia’s online marketplace stood at 15%.
However, this share declined over the years, reaching a low of 6% in 2020.
As the pandemic's impact softened, the first-party activity share started to increase again.
Standing at 13% last year, we project that this share will reach up to 16% by 2025.
Jumia's approach involves building categories in various ways across different markets, ensuring that the channel split aligns with customer value and market opportunities. This flexible strategy has allowed Jumia to adapt in the competitive market.
Stay Competitive: Our constantly updated rankings provide you with the latest insights to improve your business strategy. Discover which stores and companies are at the top of the eCommerce world and which categories are driving the highest sales. Dive into our rankings for companies, stores, and marketplaces. Stay a step ahead in the market with ECDB.
What is the Largest Market of Jumia?
We talked about how Jumia is a pan-African platform. But in which markets is Jumia thriving the most? Based on 2023 GMV:
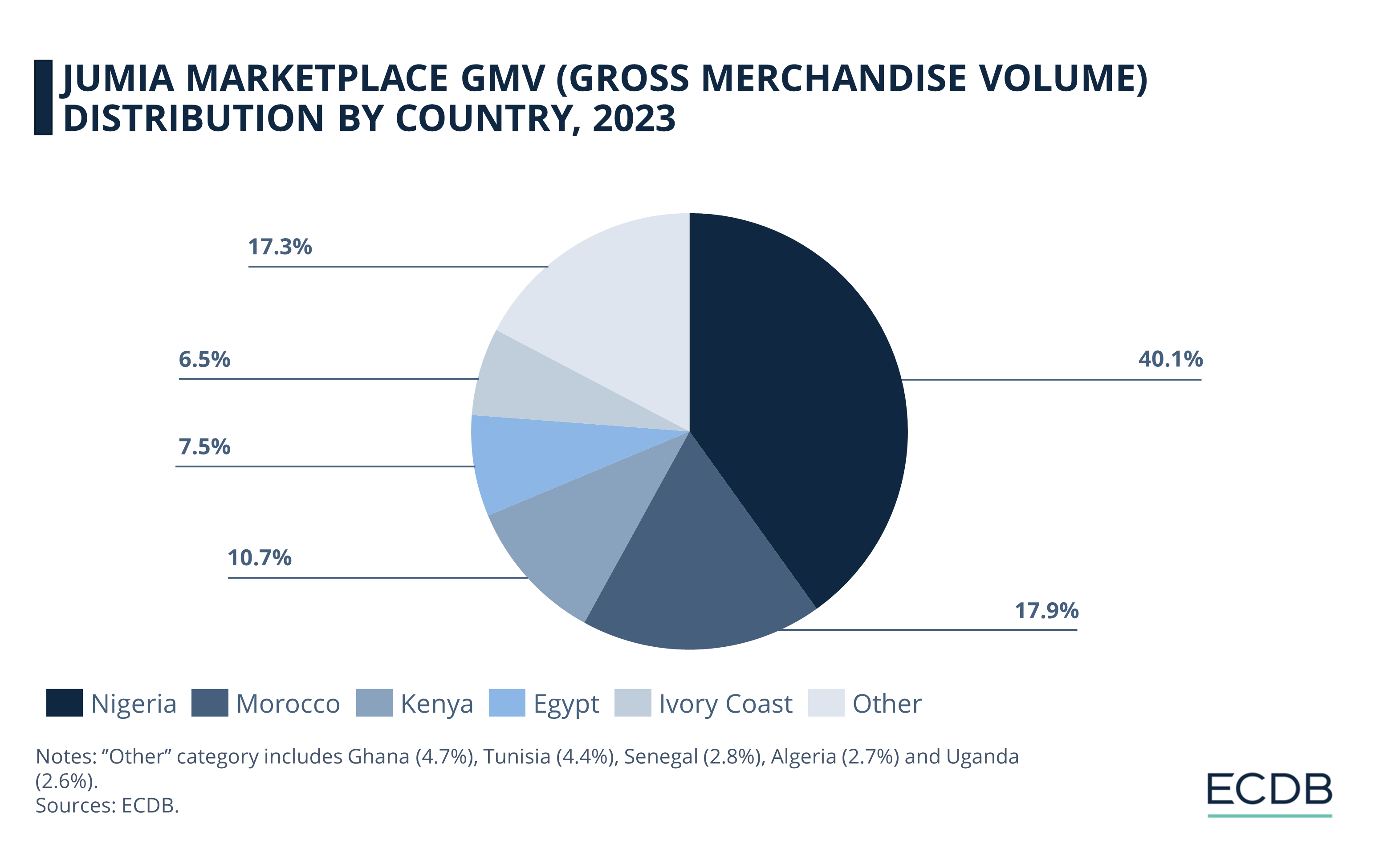
Nigeria accounts for 40.1% of the marketplace's GMV, followed by Morocco with 17.9%.
Kenya and Egypt also contribute significantly to Jumia's GMV with shares of 10.7% and 7.5% respectively.
Ivory Coast accounts for 6.5% of GMV.
The remaining 17.3% of GMV is spread across other countries, highlighting Jumia's extensive reach across different markets.

Top Jumia Domains
Building on that, how much net revenue Jumia's online stores in these countries generated in 2023 also reveals valuable insights:
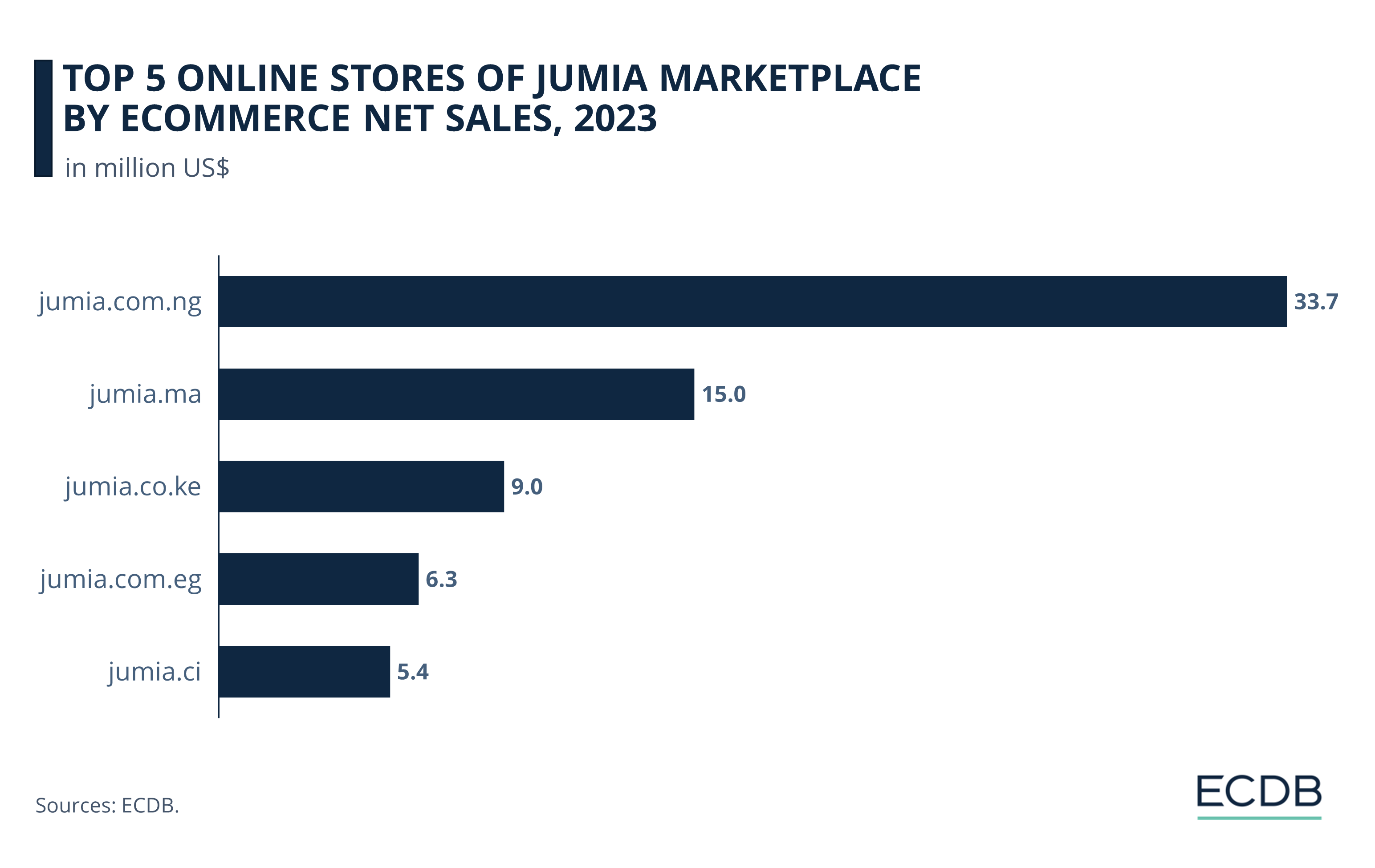
At US$33.7 million net sales in 2023 (leading the Nigerian eCommerce market), jumia.com.ng is the top Jumia online store.
Jumia’s Moroccan online store, jumia.ma, is at #2 with net sales of US$15 million.
The Kenyan domain follows at #3, having made net sales of US$9 million last year.
While Jumia’s Egyptian online store is at #4 (US$6.3 million), the Ivory Coast domain rounds out the top 5 at US$5.4 million.
What Products Sell Most on Jumia?
In 2023, electronics emerged as the top-selling product category on Jumia:
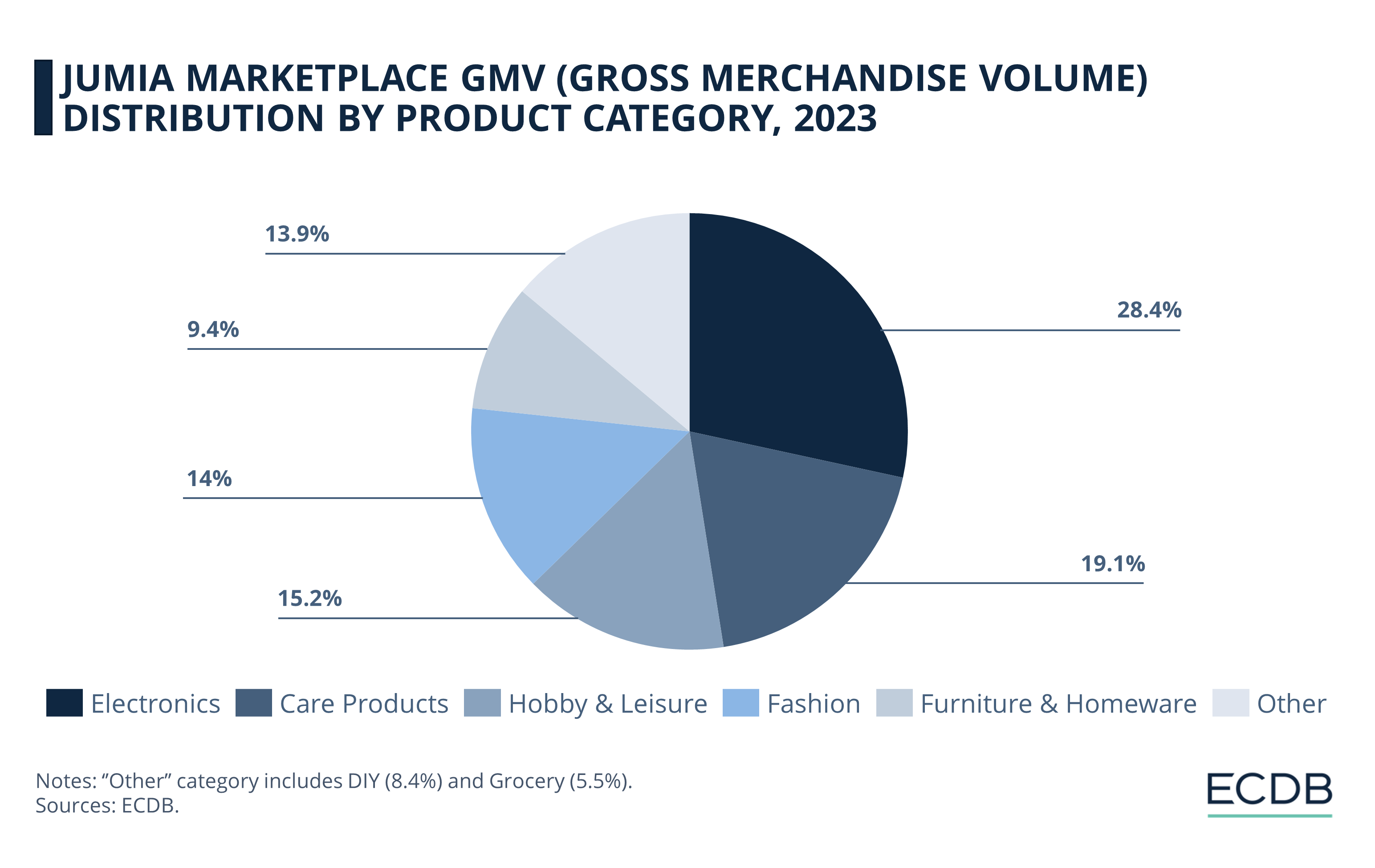
After electronics with 28.4% of the marketplace's GMV share, personal care products account for 19.1% of Jumia's GMV in 2023.
The hobby and leisure category also has a significant share at 15.2%.
Fashion items account for 14% of the GMV, while furniture and household goods contribute 9.4% of the GMV.
Zando: Jumia’s South Africa Exit
Zando, once a key part of Jumia Group and a leading online fashion retailer in South Africa, will be shutting down by the end of 2024 as part of Jumia’s restructuring efforts. The company has decided to exit non-strategic markets, including both South Africa and Tunisia, to focus on higher-growth regions such as Nigeria, Morocco, Egypt, and Kenya.
This move is aligned with Jumia’s strategy to optimize its resources and cut costs in order to improve profitability. According to CEO Francis Dufay, this decision reflects Jumia’s shift towards concentrating on its core markets, where stronger eCommerce potential exists. Despite Zando’s previous success, including a 75% GMV contribution from fashion in 2023, Jumia is prioritizing markets that offer better long-term growth prospects.
Jumia Business Analysis:
Recent Developments
Going back to Jumia, the platform has faced significant challenges and opportunities over the years. Despite a volatile economic environment, the company has shown resilience and strategic agility.
Here’s a closer look at Jumia’s financial health, strategic decisions, and key initiatives driving its growth:
Jumia’s Financial Performance
Jumia Technologies AG reported mixed financial results in the first quarter of 2024. GMV rose by 5% year-over-year to US$181.5 million, and revenue increased by 19% to US$48.9 million.
However, the company faced a loss before income tax of US$39.6 million, primarily due to currency devaluations in Nigeria and Egypt and higher finance costs. Despite these challenges, CEO Francis Dufay emphasized Jumia's strategic focus on strengthening core business and improving cash efficiency, reflecting the company's resilience amidst macroeconomic challenges in Africa.

Jumia Food: A Discontinued Effort
Jumia's food delivery service, Jumia Food, was discontinued in December 2023 across seven African countries. The decision stemmed from intense competition and challenging market conditions, with deep-pocketed rivals like Delivery Hero (Glovo) and Yandex (Yango Delivery) aggressively expanding. The market's low barriers to entry and irrational economics, such as heavy discounting and free delivery offers, made sustaining Jumia Food untenable.
Over the years, Jumia has diversified its business with other offerings than Jumia Food, such as Jumia Travel, Jumia Deals, and Jumia One.
Jumia Food once accounted for 11% of the company's GMV and was the second-largest category behind fashion. The exit from the food delivery market impacted hundreds of gig workers, leaving many struggling to find new employment opportunities. Despite its popularity, the move was part of Jumia's broader strategy to focus resources on its more profitable physical goods eCommerce segment.
JumiaPay: Driving Cashless Transactions
Jumia's proprietary payment service, JumiaPay, has become a significant driver in the company's quest for profitability.

In Q1 2024, JumiaPay transactions increased by 52% year-over-year, with total processing volume reaching US$45.4 million. The service now accounts for 32.5% of Jumia orders on physical goods, up from 20% previously.
The continued rollout of JumiaPay in key markets like Nigeria and Kenya is enhancing cashless transactions, positioning JumiaPay as a crucial enabler of Jumia's eCommerce platform.
Jumia Business Analysis: Closing Thoughts
Despite a challenging macro environment, Jumia continues to show resilience and strategic focus. The company's market cap stands strong at US$1.41 billion, with efforts to streamline operations and reduce costs yielding positive results.
As Jumia navigates currency fluctuations and competitive pressures, its focus remains on leveraging technology to connect urban and rural communities, ensuring a diverse and accessible online shopping experience across Africa.
Sources: Nasdaq, StockNews, Jumia, BBC, CompaniesMarketCap, TechCrunch, Rest of World, ECDB

Click here for
more relevant insights from
our partner Mastercard.
Related insights
Deep Dive
DM vs. Rossmann 2024: Which Online Drugstore Comes Out on Top
DM vs. Rossmann 2024: Which Online Drugstore Comes Out on Top
Deep Dive
Birkenstock Business Model: Marketing Strategy & eCommerce Sales
Birkenstock Business Model: Marketing Strategy & eCommerce Sales
Deep Dive
Kaspi to Acquire Stake in Hepsiburada, Expanding Presence in Turkey
Kaspi to Acquire Stake in Hepsiburada, Expanding Presence in Turkey
Deep Dive
How Important is eCommerce for eCommerce Giants? Analysis of Alibaba, Amazon and JD.com
How Important is eCommerce for eCommerce Giants? Analysis of Alibaba, Amazon and JD.com
Deep Dive
Amazon Enhances Online Grocery Shopping for Prime Members
Amazon Enhances Online Grocery Shopping for Prime Members
Back to main topics
